Here’s A Quick Way To Solve A Tips About How To Treat Acute Paronychia

In its earliest stage, acute paronychia may be treated with an antibiotic taken by mouth (such as dicloxacillin, cephalexin, or clindamycin) and frequent warm soaks to increase the blood flow.
How to treat acute paronychia. Wash your hands regularly, including before you apply an antifungal ointment. Can i treat paronychia at home? Infection can occur because of biting or picking at the nails.
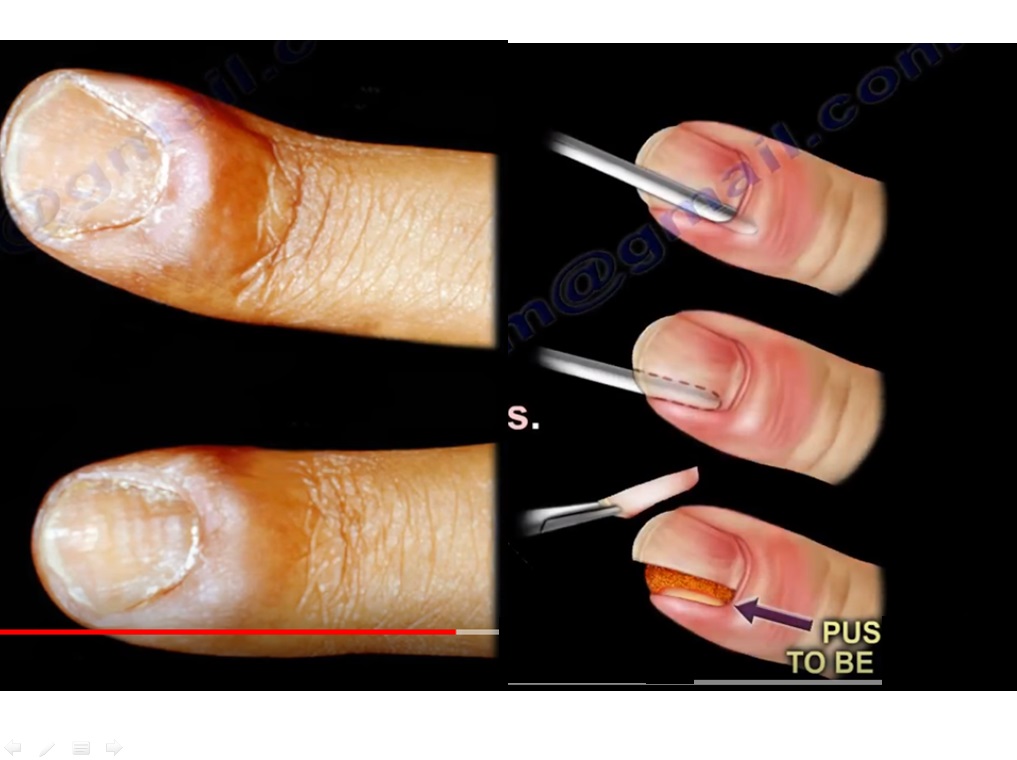
Treatment is with antistaphylococcal antibiotics and drainage of any pus. In its earliest stage, acute paronychia may be treated with an antibiotic taken by mouth (such as dicloxacillin, cephalexin, or clindamycin) and frequent warm soaks to increase the blood flow. If pus accumulates, it must be drained.
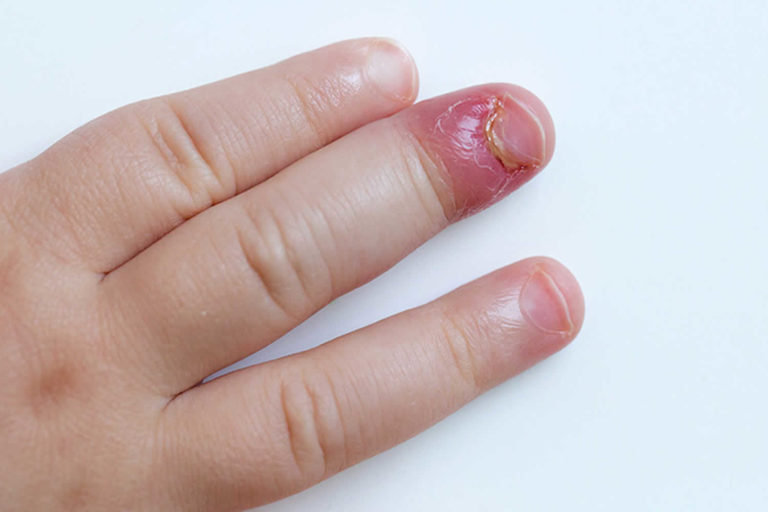
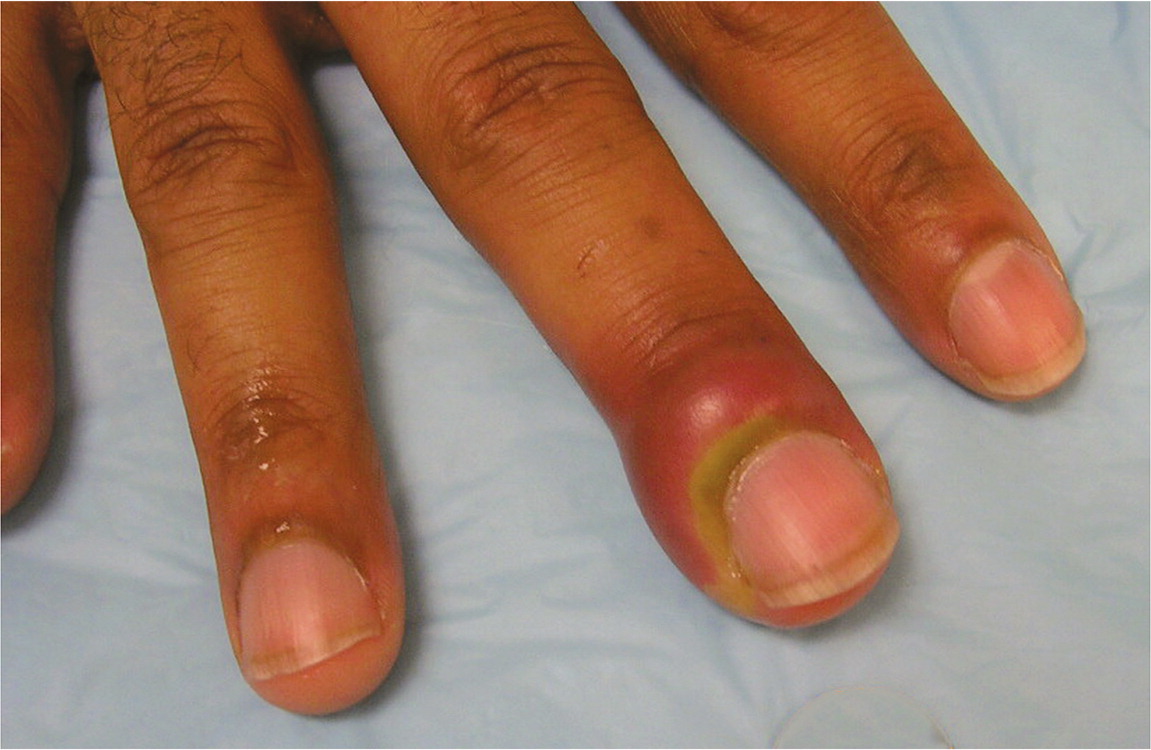
Occasionally antifungal medicines for infection caused by a yeast (candida) or a fungus are used. Left untreated, paronychia can an abscess, nail deformity, and nail loss. Definition — acute paronychia is an acute inflammatory process, with or without abscess formation, that involves the proximal and lateral nail folds and that has been present for less than six weeks.
It is usually caused by bacteria that enters a break in the skin in these areas. (use a bowl for fingers and a bigger basin for toes.) the water should be warm, but not so hot to cause pain or discomfort. Reduce pain and swelling 3.
Ask your doctor if they recommend an antifungal medication. The treatment of choice depends on the extent of the infection. 01 of 06 warm soaks fill a bowl or basin with warm tap water.
Paronychia treatment medically reviewed by poonam sachdev on april 21, 2022 written by webmd editorial contributors 1. Describe the appropriate treatment and management of paronychia. Treatment is with antistaphylococcal antibiotics and drainage of any pus.
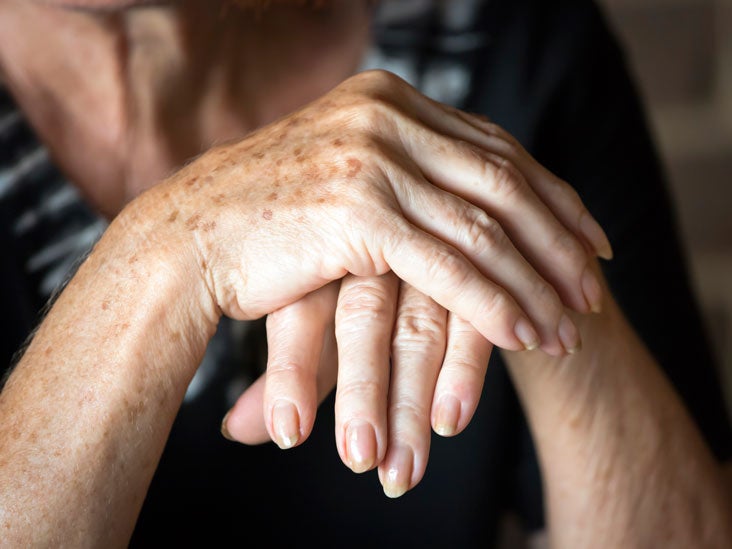
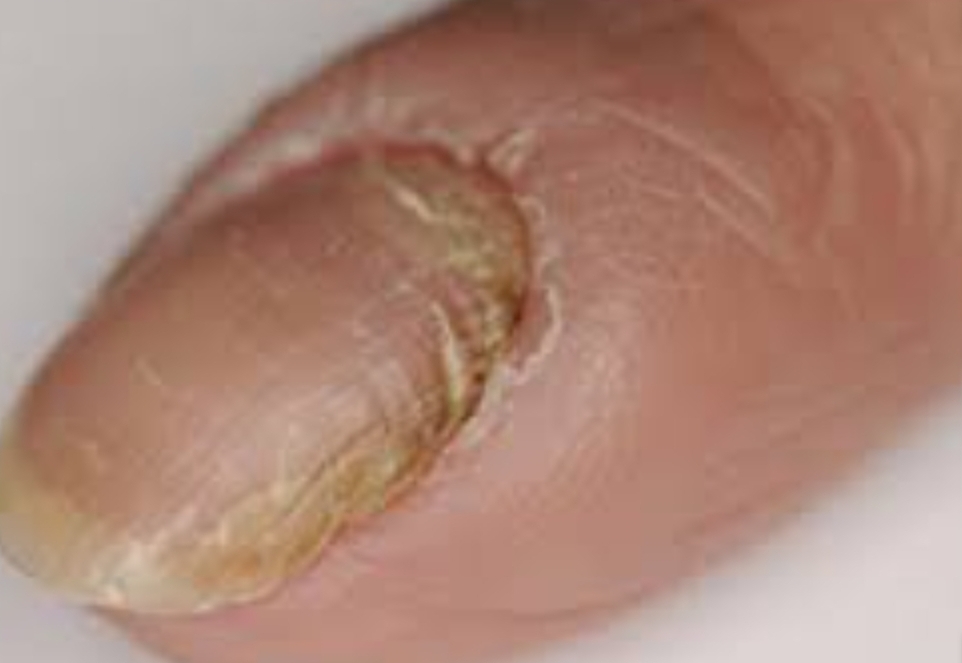
Home remedies for paronychia, or an infected nail, include soaking in warm water and applying lemon and salt. Bacteria cause acute infections, while chronic infections are most frequently associated with fungus. Acute paronychia causes redness, warmth, and pain along the nail margin.
If soft tissue swelling is present. 2 when you may need a provider Review the appropriate examination and evaluation of paronychia.
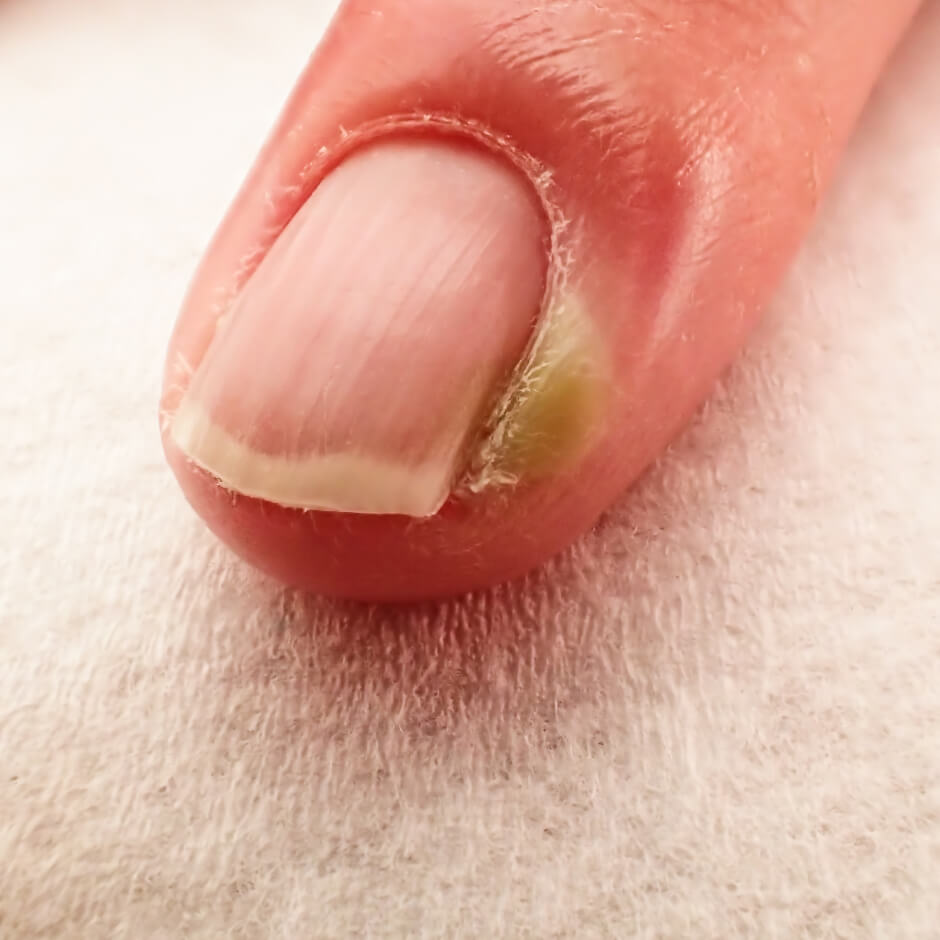
It may be acute or chronic and treatment usually involves antibiotic medicines for germ (bacterial) infections. Treatments prevention outlook bacteria, candida yeast, or a combination of the two can cause paronychia.
Treating chronic paronychia 1. Otc pain relievers like advil or tylenol can help the pain. Identify the etiology and pathophysiology of paronychia.
![What is Paronychia? [Infographic]](https://www.findatopdoc.com/var/fatd/storage/images/_aliases/infographic_main/top-videos-and-slideshows/what-is-paronychia/444066-1-eng-US/What-is-Paronychia.jpg)